What Is Resin Infusion? A Beginner’s Guide
-
Table of Contents
“Unlock the Art of Resin Infusion: A Beginner’s Guide to Crafting with Precision and Creativity.”
Resin infusion is a composite manufacturing process that involves the use of a vacuum to draw resin into a dry fiber reinforcement material, such as fiberglass or carbon fiber. This technique is widely used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and marine, due to its ability to produce lightweight, strong, and durable components. The process begins with laying out the dry fibers in a mold, followed by sealing the mold and creating a vacuum. Once the vacuum is established, resin is introduced, saturating the fibers and curing to form a solid structure. This beginner’s guide will explore the fundamentals of resin infusion, its advantages, and essential steps for successful implementation.
Understanding The Basics Of Resin Infusion
Resin infusion is a composite manufacturing process that has gained significant attention in various industries, particularly in aerospace, automotive, and marine applications. At its core, resin infusion involves the use of a liquid resin that is drawn into a dry fiber reinforcement material through a vacuum process. This method is particularly valued for its ability to produce lightweight, high-strength components while minimizing the environmental impact associated with traditional manufacturing techniques. To fully appreciate the intricacies of resin infusion, it is essential to understand its fundamental components and the process itself.
The primary materials involved in resin infusion are the fiber reinforcement and the resin. Fiber reinforcements can include materials such as glass, carbon, or aramid fibers, each offering distinct mechanical properties and performance characteristics. The choice of fiber is crucial, as it directly influences the final product’s strength, weight, and durability. On the other hand, the resin serves as the matrix that binds the fibers together, providing structural integrity and resistance to environmental factors. Common resins used in this process include epoxy, polyester, and vinyl ester, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
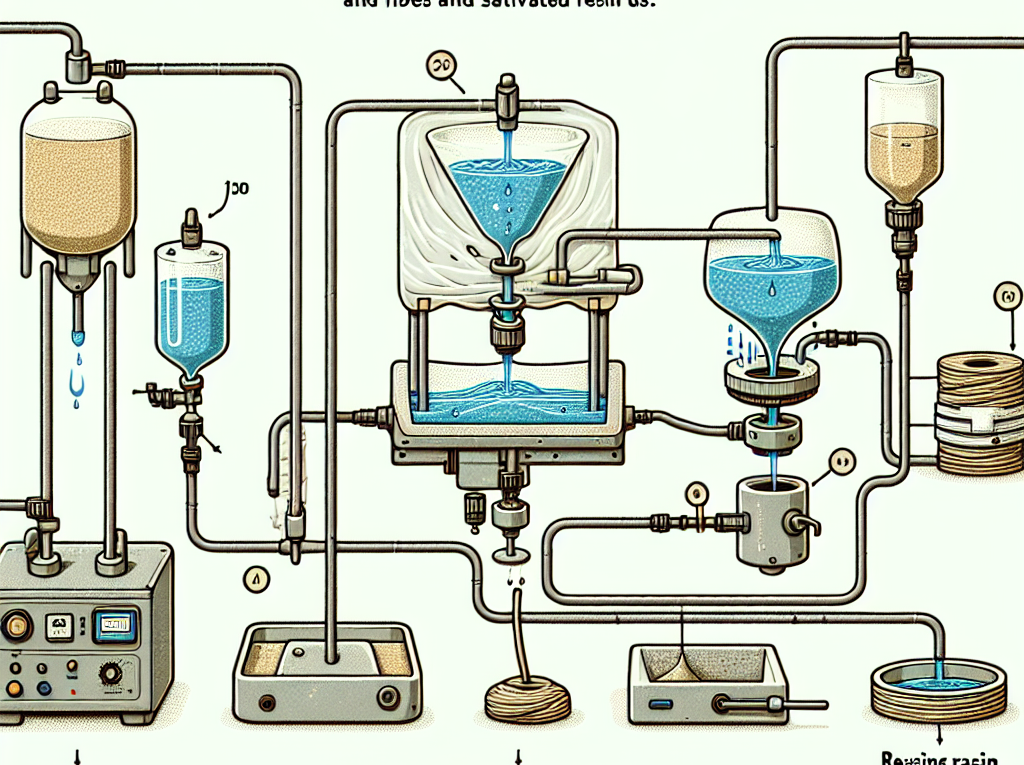
The resin infusion process begins with the preparation of the mold and the placement of the dry fiber reinforcement within it. This step is critical, as the arrangement of the fibers can significantly affect the mechanical properties of the final product. Once the fibers are positioned correctly, a vacuum bag is placed over the mold, and a vacuum is applied to remove air from the system. This vacuum not only helps to eliminate any trapped air that could compromise the integrity of the composite but also creates a pressure differential that facilitates the flow of resin into the dry fibers.
After establishing the vacuum, the resin is introduced into the system through strategically placed ports. The vacuum draws the resin into the fiber reinforcement, ensuring that it saturates the fibers evenly. This infusion process is advantageous because it allows for better control over the resin-to-fiber ratio, which is essential for achieving optimal mechanical properties. Additionally, the vacuum environment minimizes the risk of voids and air bubbles, which can weaken the composite structure.
As the resin cures, it undergoes a chemical reaction that transforms it from a liquid state into a solid matrix, effectively binding the fibers together. The curing process can be influenced by various factors, including temperature and the specific resin formulation used. Once fully cured, the composite material exhibits enhanced strength, stiffness, and resistance to environmental degradation, making it suitable for demanding applications.
One of the key benefits of resin infusion is its ability to produce large, complex parts with a high degree of precision. This capability is particularly advantageous in industries where weight reduction is critical, such as aerospace and automotive sectors. Furthermore, resin infusion is often considered a more environmentally friendly option compared to traditional methods, as it generates less waste and can utilize bio-based resins.
In conclusion, resin infusion is a sophisticated manufacturing technique that combines the benefits of advanced materials with an efficient production process. By understanding the basics of resin infusion, including the roles of fiber reinforcements and resins, as well as the steps involved in the infusion process, beginners can appreciate the potential of this technology in creating high-performance composite materials. As industries continue to seek innovative solutions for lightweight and durable components, resin infusion is poised to play a pivotal role in the future of manufacturing.
Essential Tools And Materials For Resin Infusion
Resin infusion is a sophisticated technique widely used in composite manufacturing, particularly in the production of lightweight and high-strength materials. To successfully execute this process, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of the tools and materials required. This knowledge not only enhances the quality of the final product but also ensures safety and efficiency during the infusion process.
At the core of resin infusion is the resin itself, which serves as the binding agent for the composite materials. Epoxy resin is the most commonly used type due to its excellent mechanical properties, low viscosity, and strong adhesion to various substrates. When selecting resin, it is crucial to consider the specific application, as different formulations may offer varying degrees of flexibility, heat resistance, and curing times. Additionally, hardeners or catalysts are necessary to initiate the curing process, and these should be chosen to match the resin for optimal performance.
In conjunction with the resin, the choice of reinforcement materials is equally important. Fiberglass, carbon fiber, and aramid fiber are popular options, each offering distinct advantages. Fiberglass is cost-effective and provides good strength-to-weight ratios, while carbon fiber is renowned for its exceptional stiffness and lightweight characteristics. Aramid fiber, on the other hand, is known for its impact resistance. The selection of reinforcement material will depend on the desired properties of the final composite, as well as budgetary considerations.
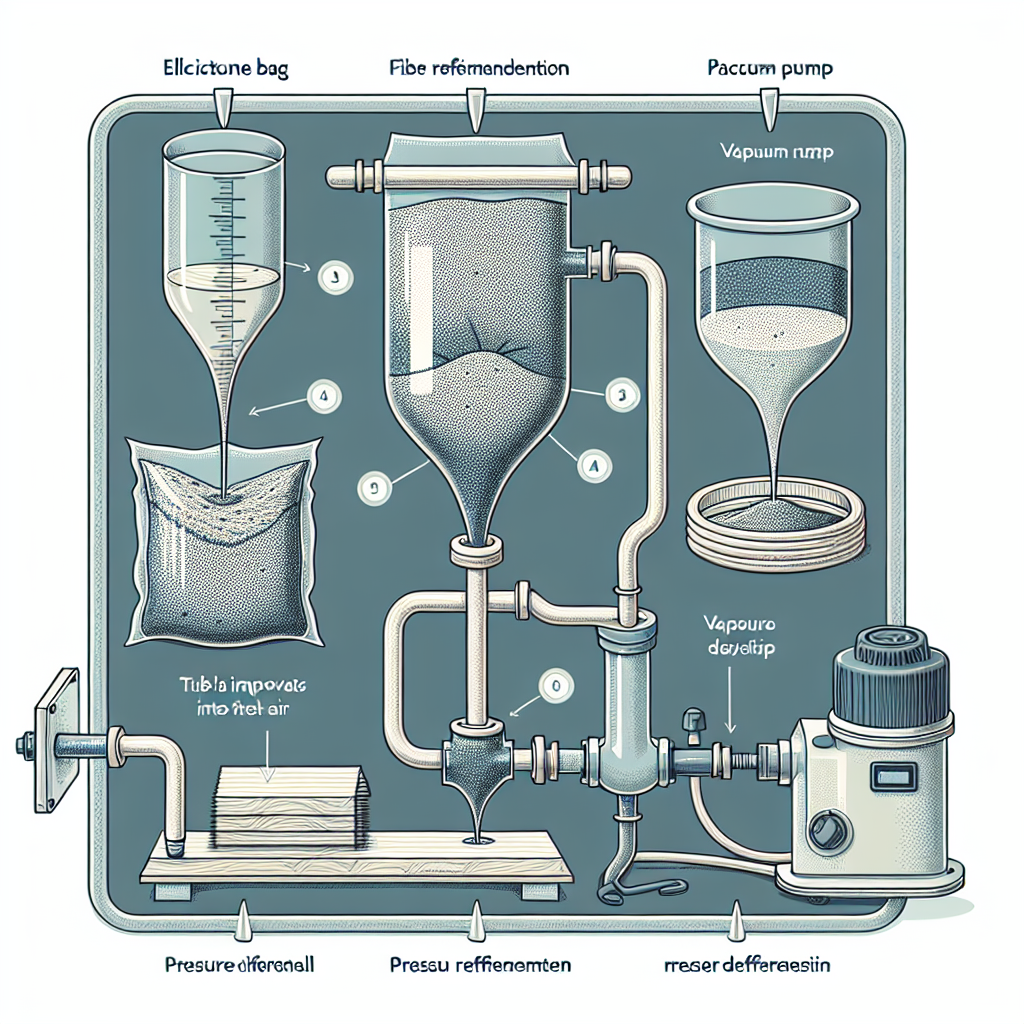
To facilitate the infusion process, a vacuum bagging system is essential. This system typically includes a vacuum pump, vacuum bag, and various sealing materials. The vacuum pump creates a low-pressure environment that helps draw the resin into the reinforcement materials, ensuring thorough saturation. The vacuum bag, made from a flexible, airtight material, encases the composite layup and maintains the necessary pressure during the infusion. Sealing materials, such as tape and sealant, are used to ensure that the vacuum bag is airtight, preventing any leaks that could compromise the infusion process.
In addition to these primary components, several ancillary tools are necessary for a successful resin infusion. Mixing containers and stir sticks are required for accurately measuring and mixing the resin and hardener. It is vital to follow the manufacturer’s instructions regarding mixing ratios to achieve the desired curing properties. Brushes or rollers may also be used to apply the resin to the reinforcement materials before the infusion begins, ensuring even distribution.
Furthermore, a variety of fittings and tubing are needed to connect the vacuum system to the infusion setup. These components allow for the controlled flow of resin into the composite layup. It is advisable to use clear tubing to monitor the resin flow visually, which can help identify any potential issues during the infusion process.
Safety equipment should not be overlooked when engaging in resin infusion. Personal protective equipment, such as gloves, goggles, and respirators, is essential to protect against harmful fumes and skin contact with the resin. Proper ventilation in the workspace is also crucial to ensure a safe working environment.
In conclusion, understanding the essential tools and materials for resin infusion is fundamental for anyone looking to embark on this intricate process. By carefully selecting the right resin, reinforcement materials, and equipment, one can achieve high-quality composite products while ensuring safety and efficiency throughout the infusion process. As with any technical endeavor, practice and experience will further enhance proficiency in resin infusion techniques.
Step-By-Step Process Of Resin Infusion Techniques
Resin infusion is a sophisticated technique widely used in composite manufacturing, particularly in the production of lightweight and high-strength materials. This method involves the process of saturating a dry fiber reinforcement with resin, allowing for the creation of robust composite structures. Understanding the step-by-step process of resin infusion is essential for beginners who wish to explore this innovative technique.
To begin with, the first step in the resin infusion process is the preparation of the mold. The mold must be clean and free of any contaminants to ensure a smooth finish on the final product. Typically, a release agent is applied to the mold surface to facilitate the easy removal of the composite once it has cured. This preparation is crucial, as any imperfections in the mold can lead to defects in the final composite structure.
Once the mold is prepared, the next step involves laying down the dry fiber reinforcement. This reinforcement can be made from various materials, such as fiberglass, carbon fiber, or aramid fiber, depending on the desired properties of the final product. The fibers are carefully arranged in the mold to achieve the required orientation and thickness. It is important to ensure that the fibers are evenly distributed and that there are no gaps, as this can affect the mechanical properties of the composite.
Following the placement of the fiber reinforcement, the infusion process can begin. A vacuum bag is then placed over the mold, and a vacuum is applied to remove any air trapped within the fibers. This step is critical, as it not only helps to compact the fibers but also prepares the system for the introduction of resin. The vacuum creates a pressure differential that will facilitate the flow of resin into the dry fibers, ensuring complete saturation.
Once the vacuum is established, the next step is to introduce the resin. This is typically done through a series of strategically placed ports that allow the resin to flow evenly throughout the fiber reinforcement. The resin is drawn into the fibers by the vacuum, which ensures that it penetrates every layer of the reinforcement. It is essential to monitor the infusion process closely, as any interruptions or inconsistencies can lead to dry spots or incomplete saturation.
As the resin flows into the fibers, it begins to cure, transforming from a liquid state to a solid state. The curing process can be accelerated by applying heat, depending on the type of resin used. During this phase, it is crucial to maintain the vacuum to ensure that the resin fully saturates the fibers and that no air is trapped within the composite. Once the resin has cured completely, the vacuum bag can be removed, and the composite can be carefully extracted from the mold.
Finally, after demolding, the composite may require additional finishing processes, such as trimming, sanding, or painting, to achieve the desired aesthetic and functional properties. This final step is essential for ensuring that the composite meets the specifications required for its intended application.
In conclusion, the resin infusion process is a meticulous yet rewarding technique that allows for the creation of high-performance composite materials. By following these steps—preparing the mold, laying down the fiber reinforcement, applying a vacuum, introducing the resin, and finally demolding—the beginner can successfully navigate the complexities of resin infusion. With practice and attention to detail, one can master this technique and unlock the potential of composite materials in various applications.
Q&A
1. **What is resin infusion?**
Resin infusion is a composite manufacturing process where a dry fiber reinforcement is placed in a mold, and a liquid resin is drawn into the fibers under vacuum pressure, allowing for the creation of strong, lightweight composite materials.
2. **What materials are commonly used in resin infusion?**
Common materials used in resin infusion include fiberglass, carbon fiber, and aramid fiber for reinforcement, along with epoxy, polyester, or vinyl ester resins as the matrix material.
3. **What are the advantages of resin infusion?**
Advantages of resin infusion include improved fiber wet-out, reduced void content, better control over resin distribution, and the ability to create complex shapes with a high strength-to-weight ratio.Resin infusion is a composite manufacturing process that involves the use of a vacuum to draw resin into a dry fiber reinforcement material, creating a strong and lightweight composite structure. This method is favored for its ability to produce high-quality parts with minimal waste and improved safety compared to traditional methods. It is commonly used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and marine. For beginners, understanding the materials, equipment, and techniques involved in resin infusion is essential for successful application and achieving desired results in composite fabrication.